Varieties of Crops and Agriculture

Crop
Carbohydrate as source of energy is obtained from cereals like wheat, rice, maize, bajra and jowar, protein is obtained from pulses like pea, gram, black lentil, urd, moong, arhar etc. and the oil- seeds like soyabean, groundnut, til (sesamum), castor, mustard, alsi (flex) and sunflower provide us with the essential fats. Vegetables, spices and condiments and fruits provide various vitamins and minerals along with some amount of proteins, fat and carbohydrates. Fodder crops like berseem, oat, grass etc. are cultivated to provide for the cattle feed. Hence, their regular production, proper management and distribution is essential to provide for the needs of the large population.
Bharat is a big country. Here climate conditions like temperature, humidity and rains vary from region to region. Hence different types of crops are cultivated in different parts of the country. Crops can be broadly categorized into two on the basis of season :
(i) Kharif crops : These are the crops which are sown during rainy season. In Bharat the rainy season is from June to September. It includes paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, moong etc.
(ii) Rabi crops : Crops grown in winter season are the rabi crops. Wheat, gram, pea, mustard and flex are some of the major rabi crops.
Varieties of Crops
Good production of crops depend upon the selection of varieties for cultivation. Various useful qualities (like disease resistance, compatibility with fertilizers, quality of the produce and high production) of the crop varieties can be chosen by breeding. Desired traits can be introduced in the varieties by hybridizations. In the hybridization technique plants with different genetic properties are hybridized. Another method of crop improvement is introduction of the desired genes. This results in the production of genetically altered varieties. Before adopting any new variety it is essential to ensure that the variety can give sufficient produce in various environments at various places. Good quality seeds should be made available to the farmers. In other words the seeds should be of the quality which germinate properly in favourable conditions.
Crop production depends upon the weather, quality of soil and availability of water. Since weather prediction like drought, floods etc. is difficult, so crops which can grow under varied environmental conditions are more useful. Similarly varieties which can grow in saline soil have also been developed for some crops. The objective of improving crop varieties includes :
- (1) High production : Increasing the production per hectare.
- (2) Improved varieties : The quality of the crop produce is different for every crop. For example the quality of protein in pulses, quality of oil in oil crops, high quantity of vitamins and minerals in fruits and vegetables etc.
- (3) Biotic and Abiotic resistance : The crop production may decrease due to various biotic (diseases, insects etc.) and abiotic (drought, salinity, water logging, heat, cold, frost etc.) factors. The varieties tolerant to these factors can increase the production under adverse conditions.
- (4) Change in maturation period : Economically it is beneficial to use varieties with reduced duration, from sowing to reaping. The farmers, hence, may obtain more than one crop produce in his field per year. Reduction in time reduces the expenses of crop production. The loss of produce is reduced if the crop maturation is simultaneous.
- (5) Broad compatibility : Production of varieties having broad compatibility will be helpful in stabilizing the produce in different environmental conditions. Some varietes may then be used for cultivation under varied environmental conditions.
- (6) Optional qualities of the crop : Long and dense branching is the desired quality for fodder crops, so that there will be more production using less of is nutrients. In this way various improved varieties may be used to enhance production.
Crop Pattern
The land becomes barren by continuous use of chemical fertilizers, insecticides and pesticides etc., therefore need was felt of techniques which could be used for crop cultivation, on a continuous basis, without harming natural resources. This is known as the long term agriculture.
Methods such as mixed farming, mixed cropping and crop-rotations are used for long-term agriculture.
- (a) Mixed farming : The needs of the farmer cannot be fulfilled by the produce of small patches of land. So the farmer adopts other methods to increase productivity. These include – animal husbandry, fisheries, horticulture and agriculture. This practice not only increases the farmer’s income but also utilizes the land available to the maximum. Mixed farming, thus, is a system of farming which involves the growing of crops along with raising the livestock.
- (b) Mixed cropping : When only one type of crop is grown in a field, the requirements of all the crop plants are alike. It will use some of the nutrients which will reduce in quantity over time while others will not be used at all. To avoid the imbalance of nutrients now-a- days two or more than two type of crops are grown together in the field. This type of cropping pattern is known as mixed cropping. For example, Wheat and gram; wheat and mustard; groundnut and sunflower etc. If due to adverse weather conditions or due to other reasons, one of the crop fails, at least the produce of the other will be available. The following things should be kept in mind while selecting crops for mixed cropping.
- One crop should be of long period while other of short period.
- One crop should be long and other should be dwarf.
- One crop should have deep root system while the other must have surface roots.
- (c) Crop Rotation : The fertility of land reduces due to continuous cropping of the same crop over the years. The production of that crop reduces due to deficiency of certain nutrients in the crop land since they are the ones being used continuously. So to replenish the soil and maintain nutrient balance, crop rotation is adopted. Crop rotation is growing of different crops in succession in the field in a planned manner. In crop rotation cultivation of cereals should be altered with the cultivation of pod-bearing leguminous plants so as to replenish the soil nitrogen.
Crop Protection
In the fields crop is affected by weeds, insects, pests and various diseases. If the pests and weeds are not controlled in time, they can cause immense harm to the crop.
Weeds are the unnecessary plants that grow along with the crop plants. For example : Vilayati Gokhru (Xanthium), Carrot-grass (Parthenium), Motha (Cyperus rotundus). These weeds compete for food space and light and use various nutrients of the soil thus reducing the production. Therefore, for healthy growth of crop plants, the weeds should be removed from the fields right from the beginning.
Usually, insect-pests attack the plants in three ways (1) they cut the roots, stem and leaves of the plants i.e. they chew them (2) they suck the cellular juices from various parts of the plant (3) they bear the fruits and stem and enter it, i.e. they perforate it. Thus they damage the crop and reduces production.
In plants diseases are caused by casual organisms like bacteria, fungi, virus etc. They are present in soil, water and air and are transmitted to the plants through them. The weeds, insects and diseases can be controlled by various methods. The most common of all is use of chemical pesticides. Various insecticides, fungicides and weedicides belong to this category. These chemicals are sprayed on the crop and are used for seed and soil treatment. But their excessive use leads to many problems. These chemicals may be toxic for plants and animals and may cause environmental pollution. Mechanically removing the weeds is another method. Preventive measures include sowing the crop on time, preparing proper beds, inter cropping and crop rotation, for controlling the growth of weeds. The pests can be controlled by using resistant varieties and ploughing the land during summer months. Deep ploughing during summer months kill the pests and uproots the weeds and exposes the seed of weeds to the heat, thus destroying them.
Methods of Irrigation
All organisms needs water to remain alive. Water is of great importance for the growth and development of flowers, fruits and seeds. Water is absorbed, along with the dissolved minerals and fertilizers from the soil, by the roots. In plants there is approximately 90% water. Water is important because seeds cannot germinate in dry conditions. The nutrients dissolved in water are translocated to all parts of the plant. It protects the plant from frost and hot air. For healthy growth of crop plants, watering the fields on a regular basis is essential. Watering the fields at different time intervals is known as irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation differs with the crop, soil type, season etc. The frequency of irrigating will be comparatively more during summer months.
Sources of Irrigation
Well, tube-well, lakes, ponds, rivers, dams and canals are the various sources of water. The methods of taking water to the fields from the sources differ from region to region.
In traditional methods cattle or workers are used. They are cheap but less efficient. They include (i) Pulley (ii) Chain pump (iii) Dhekli and (iv) Rahat (water lifting).
Water is lifted either manually or by using pumps. Diesel, biogas, electricity or solar energy is made use of to drive the pump.
Modern Methods of Irrigation
We can use water economically by using modern methods of irrigation. These methods include :
- (i) Sprinkler System : This method is used for uneven land where water availability is less. Rotating nozzles are attached to the upper ends of vertical pipes, these pipes are at a definite distance from each other and are connected to the main pipe. When water is sent to the nozzles via the vertical pipes they rotate, sprinkling water over the crop plants in a manner similar to the rains irrigating the crop.

- (ii) Drip System : In this method water reaches down directly to the roots, drop by drop. Therefore it is known as the drip system. This is the best method of irrigating the fruit trees, gardens and other plantations. Water is not wasted in this method and the plant receives continuous supply of water, drop-by- drop. This system is a boon for areas having scarcity of water.

Agriculture
Contemporary agriculture is the combined effort of arts, science and technology. In it crops with desired characteristics can be obtained using principles of science and genetic engineering. Hence the basic need of food and cloth of the fast growing human population can be met .
Various stages of advanced agriculture includes :
- (1) Improved seeds : The quality of seed is improved for more production, disease resistance, uniformity in time of maturity, adaptation for various environmental conditions.
- (2) Mineral nutrition of the crops : Crop plants need various nutrients for preparing food and for growth. Plants obtain their nutrients from air, water and soil. Different types of manure and fertilizers are used to supply nutritive elements to the soil. Dung manure, compost, vermi-compost and green manure are used as manure – Urea, di- ammonium phosphate, super phosphate, ammonium sulfate and calcium ammonium nitrate are used as fertilizers.
- (3) Weeds : Farmer sow the seeds of the crop plant but many other seeds present in the soil germinate along with the crop seeds and produce plants. The undesired plants that grow along with crop plants in the field are known as weeds.
- There is competition for water, mineral salts etc. between the crop plants and the weeds. This results in lack of availability of sufficient water and nutrients for the crop plants. The weed plants grow fast and cover the crop plant thus hindrance is generated for the sun light to reach the crop plants. Some weeds produce special chemicals from their root system and have adverse effect on the crop plants. Weeds are the shelter for various pests and pathogens and hence increases the chance of disease development. The cost of crop increases because of the cost of weeding. Weeds can be controlled physically i.e. uprooting them manually or by chemical and biological methods.
- (4) Plant diseases : Dys-functioning of the plant or any part thereof is known as the plant disease. Disease develop in plants by virus, bacteria and fungi. To control disease in crop plants, disease resistant varieties are used and pesticides are sprayed.
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is the supplementary occupation of agriculture. From ancient times man has domesticated animals and have used them. In modern times due to mechanization, the dependence of man on animals has decreased, yet animal husbandry is generating employment for a large section of our population. As compared to other countries there are maximum number of domesticated animals in Bharat and it is number one in milk production. Animal husbandry includes caring and domesticating animals such as cows, buffaloes, camels, sheep, goats, horses etc. and obtaining milk, flesh, leather, dung etc. from them and using them for agriculture.
Milk production
Milk production is an important part of the business of food products. Man has been using the milk produced by other mammals for their young ones, for his own use, since ancient times. The milk obtained from mammals, immediately after the birth of young ones is known as colostrum. In an average milk there is 87.3% water, 4.5% fat, 4.6% carbohydrate, 3.5% protein 0.75% minerals, 0.85% fat-less solid substances. The maximum protein (6.25%) is present in sheep milk and cows’ milk has about 3.21% proteins. Various products like curd, cream, butter, mawa, ghee, milk powder etc. are obtained from milk.
Because of high nutritive value bacteria grow very rapidly in milk and spoils it. Milk can be stored for many days after pasteurization and cooling.
Cattle breed
Cow, buffalo, goat etc. are domesticated for milk production. From milk production point of view the deshi varieties of cow includes Sahiwaal, Sindh, Gir, Devli, Hariyanawi etc. while the foreign breeds include Redden, Holstein, Jerry etc. The murrah, jafarabaadi, surti etc. are the varieties of buffalo preferred for more milk production. Similarly the breeds of goat are Jamanapaari, Barbery, Sirohi etc.
Animal feed
Extra animal feed should be given to bovines and pregnant cattles along with the regular feed. Animals should be fed upon 2/3 part of hay and 1/3rd green fodder. Animal feed should consist of 40% grains, 40% pomace (Khali) and 20% left over of wheat flour straining (chokar). Apart from this 50 gm of salt and 30 gms mineral powder should also be given to the cattle.
Animal health
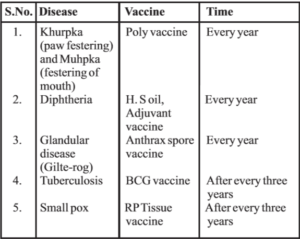
The animal should remain healthy. Production reduces in sick and unhealthy animals. For prevention of diseases animals should be vaccinated from time to time and animal shelters should be kept neat and clean. Animals may suffer from diseases caused by virus, bacteria, fungi and worms. The main diseases of animals along with their vaccines and vaccination are listed in the table given below :
Poultry Farming
The main aim of poultry farming is to obtain eggs and meat. Apart from this, by products like feathers, manure blood etc. are also obtained. The poultry industry fulfils a major part of the demand of proteins in the country, in the form of eggs and meat.
Poultry Breed
The poultry breed of Bhartiya origin includes Red jungle fowl, Aseel, Chatgoan, Bustra etc. They are reared chiefly to obtain meat. Foreign breeds (Exotic strains) includes Rhode Island Red, Plymouth Rock chicken, Leghorn, white Leghorn etc. White Leghorn is the breed with maximum egg production.
Dwelling and food
Arrangement for safe dwelling and nutritive food is essential for good growth and healthy fowls. The dwelling should be at some height. No water should be puddled near the dwelling and it should be well aerated and ventilated. Yellow maize, groundnut pomace, small wheat particles, meshed rice grains, jowar, fish powder, pebbles containing lime, salt etc. are used as food.
Health
Infectious bronchitis, Marek’s disease, Ranikhet, Plague, Small pox etc. are the main viral diseases in poultry. Proper vaccination should be done to prevent these diseases.
Apiculture
Man has been using honey obtained from honey-bee since ancient times. Honey is a high energy food stuff. It contains glucose, fructose, sucrose, minerals etc. It is used as a medicine and as a preservative. The wax obtained from bee hive is known as the bee-wax. It is used in cream, floor polish, shoe polish and sculpturing. Now-a-days, honey bee are reared to obtain honey.
Honeybee – a social insect
The form and function of honey bee varies. There are three types of honey bee in a hive. Queen, Male and worker. Queen bee can be recognized by its elongated abdomen while males have very big prominent eyes. The Queen bee dominates the hive, and controls it by secreting a substance with typical smell. The queen bee lives in the hive only. The male in their single coitus flight with the queen deposit sperms with the queen for the life-time. After this the male bees die spontaneously or they are expelled from the hive.
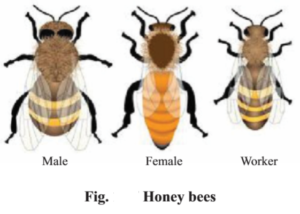
Queen bee lays two type of eggs. The generation of worker or queen from the fertilized eggs depends on their nourishment. The larvae which are fed upon the royal jelly develop into queen bee. The first formed queen bee kills the other developing queen bees. Thus there is a single queen bee in a hive. Males develop from the unfertilized eggs.
Artificial Apiculture
The main species of honey-bee includes Apis mellifera, Apis dorsata, Apis florea and Apis indica. Of these, Apis mellifera is used for Apiculture. The hives of this species are large with more accumulation of honey and the number of honey-bee is also greater. Apis dorsata is the species with sting.
For artificial Apiculture, artificial hives of the shape of closed boxes are prepared. In the artificial hives there are larger egg chambers and plates of metal or plastic. There is a coating of wax on these plates and they form the support for the formation of hives. There are many perforations in the closed box, through which the honey bee can enter the hives.
The artificial hives are placed in gardens or near the fields from where they may get the nectar. The worker bees collect the nectar and converts it into honey. Honey is collected in the cells of the artificial hive and is obtained by removing the plates from the hive.
Fishery
Fishery has been established as a profession because fishes are a good source of human nourishment. Fishes are used as a major food material. The by products of this industry includes oil rich in vitamins, protein, fins, skin scales etc. Fishery is a combined form of agriculture and animal husbandry because fishery is a type of animal husbandry while producing food from fishes in the water reservoir is agriculture.
Steps of Fish-culture
- Dwelling : Fishes are cultured in natural water sources like sea, lakes, ponds and river but artificial water reservoirs are also used for the purpose. Places with clay-rich soil are considered good for constructing water reservoir.
- Various species of fish : Fishes are produced more in fresh water as compared to that in saline water. Rohu, Mrigla, katla etc. are the indegenous fishes cultured in fisheries and common carp, silver carp etc. are the exotic species of fishes which are also cultured.
- Food for fishes : In natural water bodies minute aquatic plants and micro-organisms are the food for fishes. In artificial water bodies rice husk, particles of cereals, wheat pieces, almond pomace, soyabean etc. are provided to the fishes as food.
- Fish production : The seeds of fish (i.e. spawn) are collected with the help of nets from the breeding places of the rivers. Fertilized eggs are obtained from these seeds. The small fishes which emerge from the eggs are known as the fry. After some time fry transform into fingerlings or parr. The fingerlings are then taken to the fish cultivation tanks. Fingerlings are treated with bactericidal substances like copper sulphate, formalin, Potassium permanganate or salt to kill the infectious bacteria present there.
- Fish storage : When sufficiently big, the fishes are caught using nets in the water reservoirs or by passing current in the water body.
- Fish shielding : To prevent rotting of the fish they are preserved by burying them in ice.
Recent Post
-
Environmental Pollution : 5 Types, Effect & Causes of Pollutions and How to control on it
- Celestial bodies and Indian Calendar
- OPPO Unveils Reno8 Pro House of the Dragon Limited Edition : Book Here at lowest price, Don’t Miss it
- Yoga Sutras of Patanjali : Chapter 4: Liberation (Kaivalya Pada)
- Realme Narzo 50 5G : Buy at lowest price @ 12,999/-
- Yoga Sutras of Patanjali : Chapter 3 : Progressing (Vibhuti Pada)
- Yoga Sutras of Patanjali : Chapter 2: Practices (Sadhana Pada)
- LAVA Braze 5G : Cheapest mobile take it home. Don’t miss it
- Yoga Sutras of Patanjali : Chapter-1 : Concentration (Samadhi Pada)
- Ashtang Yog : Do you know it’s 17 Effects on Health
- Surya Namaskar : 12 Steps with pose & it’s benifits
- OPPO A98 : Full Specifications & Price in India
- Concept of Life
- Xiaomi Redmi Note 12 5G : Price, Full Specification & Launch Date
- Structure of Matter and Molecule
- Samsung Galaxy M13 5G buy at lowest price @ Rs. 9,999/-
- 7 Amazing facts about Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Mr. Rishi Sunak
- PM Kisan Tractor Yojana 2022: This Diwali, bring a free tractor at Home
- Social Media : Chapter-1, A complete free course
- Education: New Definition & Meaning and 05 Concepts
Our Partners

